Diabetic Retinopathy

Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that weakens the blood vessels that supply nourishment to the retina (the light-sensitive lining in the back of the eye where vision is focused).
These weak vessels can leak, swell or develop thin branches, causing a loss of vision. Changes to your vision may not be noticeable at first. But in its advanced stages, the disease can cause blurred or cloudy vision, floaters and blind spots – and, eventually, blindness. This damage is irreversible. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye complication and a leading cause of blindness in American adults. Macular edema, which is leaking fluid that causes blurred vision, often occurs with diabetic retinopathy.
Fortunately, diabetic retinopathy is preventable. People with diabetes are most susceptible to developing it, but your risk is reduced if you follow your prescribed diet and medications, exercise regularly, control your blood pressure, and avoid alcohol and cigarettes. Regular eye exams are an integral part of making sure your eyes are healthy. Diabetic retinopathy can be detected through a visual acuity test, a dilated eye exam or tonometry.
Although damage caused by diabetic retinopathy cannot be corrected, patients diagnosed with the condition can be treated to slow its progression and prevent further vision loss. Treatment modalities include laser and surgical procedures.
To learn more about the treatments we offer for diabetic retinopathy, please call us today to schedule an appointment.
Flashes and Floaters
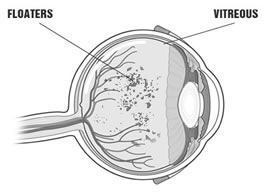
Flashes and floaters are symptoms of the eye that commonly occur as a result of age-related changes to the vitreous gel. When we are born, the vitreous is firmly attached to the retina and is a thick, firm substance without much movement.
But as we age, the vitreous becomes thinner and more watery, and tissue debris that was once secure in the firm gel can now move around inside the eye, casting shadows on the retina.
Flashes in vision occur as a result of pressure on the retina in the back of the eye, and causes patients to see flashing lights or lightning streaks. Floaters occur when fibers move across the vitreous and into your field of vision, causing patients to see specks, strands, webs or other shapes as the fibers cast shadows on the retina. These spots are most visible when looking at a plain, light background.
Although flashes and floaters are common, especially as we age, it is important to see your doctor if you experience them, as they may indicate a retinal tear or hole. Your doctor can distinguish between harmless flashes and floaters, and those that may require treatment for an underlying condition. Most flashes and floaters will become less noticeable with time as patients adjust their vision. Although these floaters are harmless, it is important to continue to receive regular eye exams to ensure that any permanent changes to your vision do not occur.
To learn more about the treatments for flashes and floaters provided at our practice, please call 662.328.2061 today to schedule an appointment.
